1 引言
与组件生命周期绑定的 Utils 非常适合基于 React Hooks 来做,比如可以将 “发请求” 这个功能与组件生命周期绑定,实现一些便捷的功能。
这次以 @umijs/use-request 为例子,分析其功能思路与源码。
2 简介
@umijs/use-request 支持以下功能:
- 默认自动请求:在组件初次加载时自动触发请求函数,并自动管理
loading,data,error状态。 - 手动触发请求:设置
options.manual = true, 则手动调用run时才会取数。 - 轮询请求:设置
options.pollingInterval则进入轮询模式,可通过run/cancel开始与停止轮询。 - 并行请求:设置
options.fetchKey可以对请求状态隔离,通过fetches拿到所有请求状态。 - 请求防抖:设置
options.debounceInterval开启防抖。 - 请求节流:设置
options.throttleInterval开启节流。 - 请求缓存 & SWR:设置
options.cacheKey后开启对请求结果缓存机制,下次请求前会优先返回缓存并在后台重新取数。 - 请求预加载:由于
options.cacheKey全局共享,可以提前执行run实现预加载效果。 - 屏幕聚焦重新请求:设置
options.refreshOnWindowFocus = true在浏览器refocus与revisible时重新请求。 - 请求结果突变:可以通过
mutate直接修改取数结果。 - 加载延迟:设置
options.loadingDelay可以延迟loading变成true的时间,有效防止闪烁。 - 自定义请求依赖:设置
options.refreshDeps可以在依赖变动时重新触发请求。 - 分页:设置
options.paginated可支持翻页场景。 - 加载更多:设置
options.loadMore可支持加载更多场景。
一切 Hooks 的功能拓展都要基于 React Hooks 生命周期,我们可以利用 Hooks 做下面几件与组件相关的事:
- 存储与当前组件实例绑定的 mutable、immutable 数据。
- 主动触发调用组件 rerender。
- 访问到组件初始化、销毁时机的钩子。
上面这些功能就可以基于这些基础能力拓展了:
默认自动请求
在组件初始时机取数。由于和组件生命周期绑定,可以很方便实现各组件相互隔离的取数顺序强保证:可以利用取数闭包存储 requestIndex,取数结果返回后与当前最新 requestIndex 进行比对,丢弃不一致的取数结果。
手动触发请求
将触发取数的函数抽象出来并在 CustomHook 中 return。
轮询请求
在取数结束后设定 setTimeout 重新触发下一轮取数。
并行请求
每次取数时先获取当前请求唯一标识 fetchKey,仅更新这个 key 下的状态。
请求防抖、请求节流
这个实现方式可以挺通用化,即取数调用函数处替换为对应 debounce 或 throttle 函数。
请求预加载
这个功能只要实现全局缓存就自然支持了。
屏幕聚焦重新请求
这个可以统一监听 window action 事件,并触发对应组件取数。可以全局统一监听,也可以每个组件分别监听。
请求结果突变
由于取数结果存储在 CustomHook 中,直接修改数据 data 值即可。
加载延迟
有加载延迟时,可以先将 loading 设置为 false,等延迟到了再设置为 true,如果此时取数提前完毕则销毁定时器,实现无 loading 取数。
自定义请求依赖
利用 useEffect 和自带的 deps 即可。
分页
基于通用取数 Hook 封装,本质上是多带了一些取数参数与返回值参数,并遵循 Antd Table 的 API。
加载更多
和分页类似,区别是加载更多不会清空已有数据,并且需要根据约定返回结构 noMore 判断是否能继续加载。
3 精读
接下来是源码分析。
首先定义了一个类 Fetch,这是因为一个 useRequest 的 fetchKey 特性可以通过多实例解决。
Class 的生命周期不依赖 React Hooks,所以将不依赖生命周期的操作收敛到 Class 中,不仅提升了代码抽象程度,也提升了可维护性。
class Fetch<R, P extends any[]> {
// ...
// 取数状态存储处
state: FetchResult<R, P> = {
loading: false,
params: [] as any,
data: undefined,
error: undefined,
run: this.run.bind(this.that),
mutate: this.mutate.bind(this.that),
refresh: this.refresh.bind(this.that),
cancel: this.cancel.bind(this.that),
unmount: this.unmount.bind(this.that),
};
constructor(
service: Service<R, P>,
config: FetchConfig<R, P>,
// 外部通过这个回调订阅 state 变化
subscribe: Subscribe<R, P>,
initState?: { data?: any; error?: any; params?: any; loading?: any }
) {}
// 此 setState 非彼 setState,作用是更新 state 并通知订阅
setState(s = {}) {
this.state = {
...this.state,
...s,
};
this.subscribe(this.state);
}
// 实际取数函数,但下划线命名的带有一些历史气息啊
_run(...args: P) {}
// 对外暴露的取数函数,对防抖和节流做了分发处理
run(...args: P) {
if (this.debounceRun) {
// return ..
}
if (this.throttleRun) {
// return ..
}
return this._run(...args);
}
// 取消取数,考虑到了防抖、节流兼容性
cancel() {}
// 以上次取数参数重新取数
refresh() {}
// 轮询 starter
rePolling() {}
// 对应 mutate 函数
mutate(data: any) {}
// 销毁订阅
unmount() {}
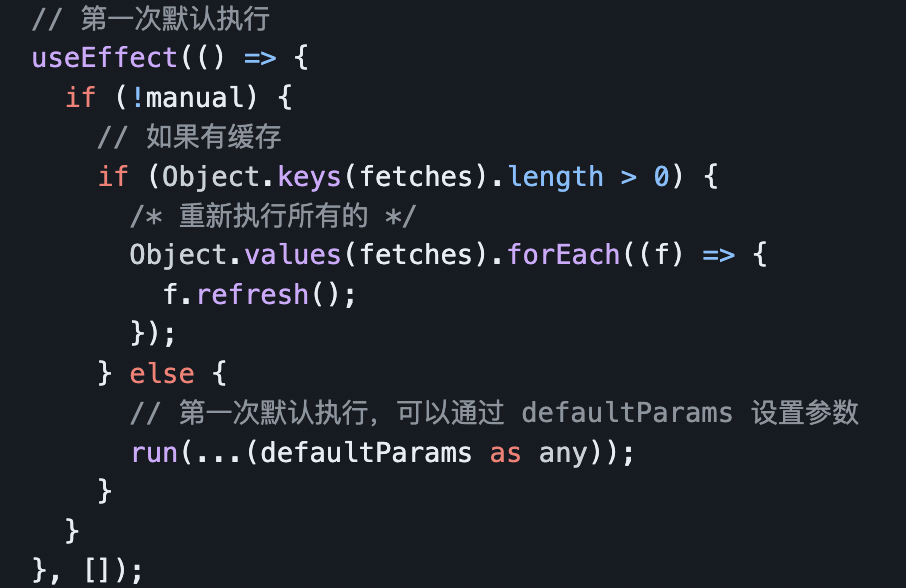
}默认自动请求
通过 useEffect 零依赖实现,需要:
- 有缓存则不需响应,当对应缓存结束后会通知,同时也支持了请求预加载功能。
- 为支持并行请求,所有请求都通过
fetches独立管理。
// 第一次默认执行
useEffect(() => {
if (!manual) {
// 如果有缓存
if (Object.keys(fetches).length > 0) {
/* 重新执行所有的 */
Object.values(fetches).forEach((f) => {
f.refresh();
});
} else {
// 第一次默认执行,可以通过 defaultParams 设置参数
run(...(defaultParams as any));
}
}
}, []);默认执行第 11 行,并根据当前的 fetchKey 生成对应 fetches,如果初始化已经存在 fetches,则行为改为重新执行所有 已存在的 并行请求。
手动触发请求
上一节已经在初始请求时禁用了 manual 开启时的默认取数。下一步只要将封装的取数函数 run 定义出来并暴露给用户:
const run = useCallback(
(...args: P) => {
if (fetchKeyPersist) {
const key = fetchKeyPersist(...args);
newstFetchKey.current = key === undefined ? DEFAULT_KEY : key;
}
const currentFetchKey = newstFetchKey.current;
// 这里必须用 fetchsRef,而不能用 fetches。
// 否则在 reset 完,立即 run 的时候,这里拿到的 fetches 是旧的。
let currentFetch = fetchesRef.current[currentFetchKey];
if (!currentFetch) {
const newFetch = new Fetch(
servicePersist,
config,
subscribe.bind(null, currentFetchKey),
{
data: initialData,
}
);
currentFetch = newFetch.state;
setFeches((s) => {
// eslint-disable-next-line no-param-reassign
s[currentFetchKey] = currentFetch;
return { ...s };
});
}
return currentFetch.run(...args);
},
[fetchKey, subscribe]
);主动取数函数与内部取数函数共享一个,所以 run 函数要考虑多种情况,其中之一就是并行取数的情况,因此需要拿到当前取数的 fetchKey,并创建一个 Fetch 的实例,最终调用 Fetch 实例的 run 函数取数。
轮询请求
轮询取数在 Fetch 实际取数函数 _fetch 中定义,当取数函数 fetchService(对多种形态的取数方法进行封装后)执行完后,无论正常还是报错,都要进行轮询逻辑,因此在 .finally 时机里判断:
fetchService.then().finally(() => {
if (!this.unmountedFlag && currentCount === this.count) {
if (this.config.pollingInterval) {
// 如果屏幕隐藏,并且 !pollingWhenHidden, 则停止轮询,并记录 flag,等 visible 时,继续轮询
if (!isDocumentVisible() && !this.config.pollingWhenHidden) {
this.pollingWhenVisibleFlag = true;
return;
}
this.pollingTimer = setTimeout(() => {
this._run(...args);
}, this.config.pollingInterval);
}
}
});轮询还要考虑到屏幕是否隐藏,如果可以触发轮询则触发定时器再次调用 _run,注意这个定时器需要正常销毁。
并行请求
每个 fetchKey 对应一个 Fetch 实例,这个逻辑在 手动触发请求 介绍的 run 函数中已经实现。
这块的封装思路可以品味一下,从外到内分别是 React Hooks 的 fetch -> Fetch 类的 run -> Fetch 类的 _run,并行请求做在 React Hooks 这一层。
请求防抖、请求节流
这个实现就在 Fetch 类的 run 函数中:
function run(...args: P) {
if (this.debounceRun) {
this.debounceRun(...args);
return Promise.resolve(null as any);
}
if (this.throttleRun) {
this.throttleRun(...args);
return Promise.resolve(null as any);
}
return this._run(...args);
}由于防抖和节流是 React 无关的,也不是最终取数无关的,因此实现在 run 这个夹层函数进行分发。
这里实现的比较简化,防抖后 run 拿到的 Promise 不再是有效的取数结果了,其实这块还是可以进一步对 Promise 进行封装,无论在防抖还是正常取数的场景都返回 Promise,只需 resolve 的时机由 Fetch 这个类灵活把控即可。
请求预加载
预加载就是缓存机制,首先利用 useEffect 同步缓存:
// cache
useEffect(() => {
if (cacheKey) {
setCache(cacheKey, {
fetches,
newstFetchKey: newstFetchKey.current,
});
}
}, [cacheKey, fetches]);在初始化 Fetch 实例时优先采用缓存:
const [fetches, setFeches] = useState<Fetches<U, P>>(() => {
// 如果有 缓存,则从缓存中读数据
if (cacheKey) {
const cache = getCache(cacheKey);
if (cache) {
newstFetchKey.current = cache.newstFetchKey;
/* 使用 initState, 重新 new Fetch */
const newFetches: any = {};
Object.keys(cache.fetches).forEach((key) => {
const cacheFetch = cache.fetches[key];
const newFetch = new Fetch();
// ...
newFetches[key] = newFetch.state;
});
return newFetches;
}
}
return [];
});屏幕聚焦重新请求
在 Fetch 构造函数实现监听并调用 refresh 即可,源码里采取全局统一监听的方式:
function subscribe(listener: () => void) {
listeners.push(listener);
return function unsubscribe() {
const index = listeners.indexOf(listener);
listeners.splice(index, 1);
};
}
let eventsBinded = false;
if (typeof window !== "undefined" && window.addEventListener && !eventsBinded) {
const revalidate = () => {
if (!isDocumentVisible()) return;
for (let i = 0; i < listeners.length; i++) {
// dispatch 每个 listener
const listener = listeners[i];
listener();
}
};
window.addEventListener("visibilitychange", revalidate, false);
// only bind the events once
eventsBinded = true;
}在 Fetch 构造函数里注册:
this.limitRefresh = limit(this.refresh.bind(this), this.config.focusTimespan);
if (this.config.pollingInterval) {
this.unsubscribe.push(subscribeVisible(this.rePolling.bind(this)));
}并通过 limit 封装控制调用频率,并 push 到 unsubscribe 数组,一边监听可以随组件一起销毁。
请求结果突变
这个函数只要更新 data 数据结果即可:
function mutate(data: any) {
if (typeof data === "function") {
this.setState({
data: data(this.state.data) || {},
});
} else {
this.setState({
data,
});
}
}值得注意的是,cancel、refresh、mutate 都必须在初次请求完成后才有意义,所以初次返回的函数是一个抛错:
const noReady = useCallback(
(name: string) => () => {
throw new Error(`Cannot call ${name} when service not executed once.`);
},
[]
);
return {
loading: !manual || defaultLoading,
data: initialData,
error: undefined,
params: [],
cancel: noReady("cancel"),
refresh: noReady("refresh"),
mutate: noReady("mutate"),
...(fetches[newstFetchKey.current] || {}),
} as BaseResult<U, P>;等取数完成后会被 ...(fetches[newstFetchKey.current] || {}) 这一段覆盖为正常函数。
加载延迟
如果设置了加载延迟,请求发动时就不应该立即设置为 loading,这个逻辑写在 _run 函数中:
function _run(...args: P) {
// 取消 loadingDelayTimer
if (this.loadingDelayTimer) {
clearTimeout(this.loadingDelayTimer);
}
this.setState({
loading: !this.config.loadingDelay,
params: args,
});
if (this.config.loadingDelay) {
this.loadingDelayTimer = setTimeout(() => {
this.setState({
loading: true,
});
}, this.config.loadingDelay);
}
}启动一个 setTimeout 将 loading 设为 true 即可,这个 timeout 在下次执行 _run 时被 clearTimeout 清空。
自定义请求依赖
最明智的做法是利用 useEffect 实现,实际代码做了组件 unmount 保护:
// refreshDeps 变化,重新执行所有请求
useUpdateEffect(() => {
if (!manual) {
/* 全部重新执行 */
Object.values(fetchesRef.current).forEach((f) => {
f.refresh();
});
}
}, [...refreshDeps]);非手动条件下,依赖变化所有已存在的 fetche 执行 refresh 即可。
分页和加载更多就不解析了,原理是在 useAsync 这个基础请求 Hook 基础上再包一层 Hook,拓展取数参数与返回结果。
4 总结
目前还有 错误重试、请求超时管理、Suspense 没有支持,看完这篇精读后,相信你已经可以提 PR 了。
1、本站所有资源均从互联网上收集整理而来,仅供学习交流之用,因此不包含技术服务请大家谅解!
2、本站不提供任何实质性的付费和支付资源,所有需要积分下载的资源均为网站运营赞助费用或者线下劳务费用!
3、本站所有资源仅用于学习及研究使用,您必须在下载后的24小时内删除所下载资源,切勿用于商业用途,否则由此引发的法律纠纷及连带责任本站和发布者概不承担!
4、本站站内提供的所有可下载资源,本站保证未做任何负面改动(不包含修复bug和完善功能等正面优化或二次开发),但本站不保证资源的准确性、安全性和完整性,用户下载后自行斟酌,我们以交流学习为目的,并不是所有的源码都100%无错或无bug!如有链接无法下载、失效或广告,请联系客服处理!
5、本站资源除标明原创外均来自网络整理,版权归原作者或本站特约原创作者所有,如侵犯到您的合法权益,请立即告知本站,本站将及时予与删除并致以最深的歉意!
6、如果您也有好的资源或教程,您可以投稿发布,成功分享后有站币奖励和额外收入!
7、如果您喜欢该资源,请支持官方正版资源,以得到更好的正版服务!
8、请您认真阅读上述内容,注册本站用户或下载本站资源即您同意上述内容!
原文链接:https://www.shuli.cc/?p=17920,转载请注明出处。


评论0